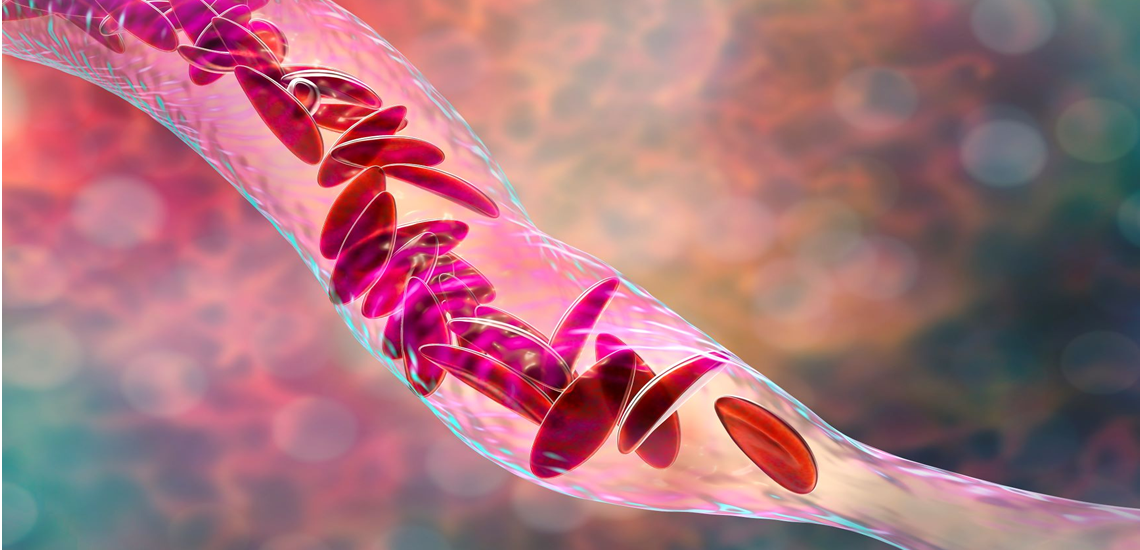
Sickle cell anemia is a genetic blood disorder characterized by the production of abnormal hemoglobin, called hemoglobin S. This condition predominantly affects individuals of African, Mediterranean, Middle Eastern, and Indian descent.
In sickle cell anemia, red blood cells become rigid and shaped like a crescent or sickle, rather than the normal disc shape. These misshapen cells can lead to various health complications, including anemia, pain crises, and increased risk of infections. The sickle cells can obstruct blood flow, resulting in pain and potential damage to organs.
Symptoms often appear in early childhood and can include fatigue, jaundice, and episodes of severe pain, known as vaso-occlusive crises. Regular medical care is crucial for managing the disease, which may include pain management, blood transfusions, and medications like hydroxyurea to reduce complications.
Education and awareness about sickle cell anemia are vital for early diagnosis and treatment. Genetic counseling is also recommended for families at risk. Despite the challenges, many individuals with sickle cell anemia lead fulfilling lives with proper medical care and support.
In conclusion, sickle cell anemia is a significant health concern that requires ongoing attention and research to improve the quality of life for those affected.



0 Comments